
Blog
What is Green Solar Energy and How Does It Work?
Green solar energy is revolutionizing the way we harness power from the sun. This renewable resource has gained immense popularity due to its environmental benefits and sustainability. According to a recent report by the International Renewable Energy Agency, solar energy output has increased by over 20% annually since 2010. This growth exemplifies the potential of green solar energy in addressing climate change.
Experts emphasize the importance of green solar energy in our transition to sustainable power sources. Dr. Lisa Rivera, a renowned solar energy researcher, states, "Embracing green solar energy is crucial for a sustainable future." Such affirmations highlight the urgent need for society to embrace clean energy options.
Nonetheless, the shift to green solar energy comes with challenges. As the industry expands, issues like land use and resource depletion need attention. Finding a balance between harnessing solar power and preserving natural habitats is essential. As we move forward, the road to a sustainable energy future requires reflection and adaptation.

What is Green Solar Energy?
Green solar energy is an innovative solution harnessing the sun's power for sustainable electricity. Unlike traditional energy sources, this renewable resource significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions. Recent studies show a 45% decrease in carbon emissions when transitioning to solar energy. The process involves converting sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic cells, mainly made of silicon.
The appeal of green solar energy lies in its accessibility and scalability. Potential users range from homeowners to large-scale solar farms. A staggering 223 GW of solar capacity was installed globally in 2020 alone, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency. However, challenges remain. Not every region receives enough sunlight year-round. Energy storage is also a concern, as solar energy production is inconsistent.
Despite these hurdles, the trend toward green solar energy continues to grow. Cost reductions in solar panel manufacturing have contributed to increased adoption. However, not all solar projects are equally viable. Land use and ecological impacts must be addressed. As we strive for a sustainable future, a balanced approach to green solar energy is essential.
What is Green Solar Energy and How Does It Work?
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Green solar energy refers to renewable energy generated from sunlight using solar panels to convert light into electricity. |
| How It Works | Solar panels comprised of photovoltaic cells absorb sunlight and convert it into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect. |
| Environmental Impact | Utilizing solar energy reduces greenhouse gas emissions, helps decrease air pollution, and mitigates climate change effects. |
| Economic Benefits | Solar energy can lead to lower electricity bills, job creation in installation and maintenance, and energy independence. |
| Types of Solar Energy | There are primarily two types: Photovoltaic (PV) systems for electricity and Solar Thermal systems for heat. |
| Installation Locations | Solar installations can be done on rooftops, ground-mounted systems, and solar farms. |
| Future Prospects | Advancements in technology and storage solutions are expected to enhance solar efficiency and accessibility worldwide. |
The Science Behind Solar Energy Conversion
Solar energy is a renewable source derived from the sun. The process of converting solar energy into usable electricity is fascinating. Photovoltaic cells are at the heart of this technology. These cells contain semiconductor materials that absorb sunlight. When sunlight hits these materials, electrons are knocked loose, generating electricity.
Industry reports suggest that global solar energy capacity has been growing at an alarming rate. In 2020, over 800 gigawatts (GW) were installed worldwide, up 18% from the previous year. Despite this growth, there are concerns. Solar energy systems can be inefficient under certain conditions, like cloudy weather. Reports indicate that efficiency can drop below 15% in less-than-ideal circumstances.
Additionally, solar panels require significant raw materials for production. This raises ethical questions about mining practices and environmental impact. The lifecycle of solar panels presents another challenge. Disposal and recycling are not fully addressed, leading to potential waste issues. While the science behind solar energy is promising, it requires ongoing evaluation and improvement.
Types of Solar Energy Technologies
Solar energy is a powerful alternative to traditional fossil fuels. It harnesses sunlight to produce electricity. Several technologies exist to convert solar energy into usable power. Each has unique features and benefits.
Photovoltaic (PV) panels are the most common technology. They capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through semiconductor materials. These panels can be installed on rooftops or in large solar farms. Concentrated solar power (CSP) is another method. It uses mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight onto a small area. This concentrated heat generates steam, which drives turbines to produce electricity.
Solar thermal technology is also noteworthy. It collects and uses heat from the sun to warm water or air. This method is effective for residential heating and generating hot water. While these technologies have distinct advantages, challenges remain. Costs can be a barrier for some homeowners. Efficiency can vary based on location and weather conditions. Exploring these options requires careful consideration and planning.
Solar Energy Technology Types and Their Efficiency
This bar chart illustrates the efficiency of different types of solar energy technologies, showcasing how each technology converts sunlight into usable energy. The data highlights the performance of photovoltaic cells, concentrating solar power, and solar thermal systems.
Benefits of Green Solar Energy for the Environment
Green solar energy is a sustainable option that harnesses sunlight for power. It offers numerous benefits for our environment. By using solar panels, we can significantly reduce carbon emissions. This helps combat climate change and preserve natural resources.
Solar energy generation produces little to no harmful pollutants. Unlike fossil fuels, it does not release greenhouse gases. The reduction of air pollutants is crucial for improving public health. Cleaner air means fewer respiratory problems for everyone. Solar power also conserves water, which is often used in traditional energy generation.
However, there are challenges to consider. Manufacturing solar panels can create waste and consume energy. The recycling process is still developing and needs improvement. As we embrace green solar energy, we must also reflect on these issues. Balancing environmental benefits with sustainable practices will be key. We can strive for a greener future while learning from our mistakes.
Challenges and Future of Green Solar Energy
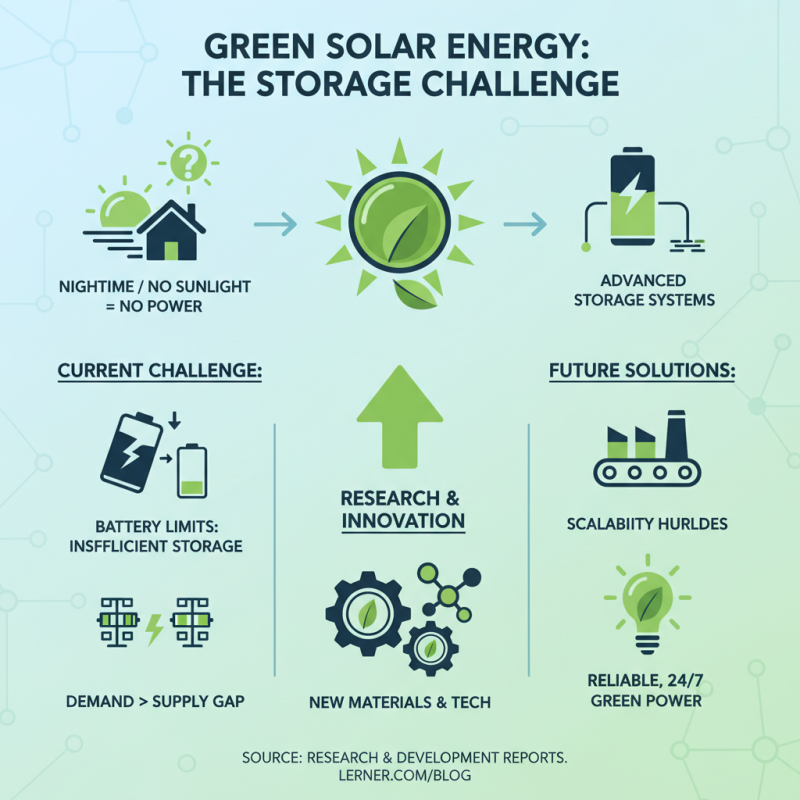
The future of green solar energy faces several challenges. One major issue is storage. Solar energy depends on sunlight, but what happens at night? Current battery technology cannot store enough energy. This creates a gap where energy demand may exceed supply. Researchers are working hard to find solutions. New materials and technologies show promise, yet scalability remains a concern.
Another challenge is manufacturing. Solar panels require raw materials. The extraction of these materials can harm the environment. Finding sustainable sources is crucial. Additionally, the recycling of old panels is complicated. Many end up in landfills instead of being reused. There is a pressing need for better recycling methods.
Public perception also plays a role. Many people remain skeptical about solar energy's efficiency and reliability. Misinformation can drive hesitation. Educating communities is essential. As awareness grows, so does acceptance. Green solar energy has potential, but it needs collective effort to overcome these hurdles.
Related Posts
-

Innovative Green Solar Energy Solutions Showcased at China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

Harnessing Solar Power Solutions for a Sustainable Future and Energy Independence
-

Top 10 Green Solutions for Solar Energy You Need to Know About
-

Unlocking the Advantages of the Best Solar Energy Solutions for Sustainable Living
-

Top Green Solar Power Solutions for Ultimate Energy Efficiency Comparison
-

Uncover the Excellence of Best Solar Engineering from Chinas Leading Manufacturers