
Blog
How to Harness Solar Power for Your Home Energy Needs?
Harnessing solar power for home energy needs is increasingly popular. Many homeowners are looking for sustainable solutions. Solar power offers a clean and renewable energy source. It reduces dependence on fossil fuels and lowers electricity bills.
Installing solar panels can seem overwhelming. Various components and installation requirements may confuse potential users. However, understanding the basic principles can simplify the process. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, making them efficient energy producers.
Embracing solar power comes with its challenges. Initial costs can be high, and maintenance is necessary. Some people may wonder if solar power is worth the investment. Nevertheless, the long-term benefits often outweigh these concerns. Making this transition can lead to energy independence and reduced carbon footprints.

Understanding Solar Energy: Basics and Importance for Home Energy Needs
Solar energy is becoming a vital resource for homeowners. It provides a sustainable way to meet energy needs and reduce electricity bills. In recent years, the cost of solar panels has dropped by over 80%, making it more accessible. Reports show that solar energy could power 40% of U.S. homes by 2035. This shift is both economical and essential for the environment.
The basics of solar energy revolve around photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells convert sunlight into electricity. The system can be installed on rooftops or as ground-mounted panels. One challenge is that solar energy generation fluctuates throughout the day. Homeowners may need battery storage systems to cover their energy needs at night.
Tips: Start by assessing your home's solar potential. Look for shading issues and consider your roof's orientation. Understand your energy consumption patterns, as this helps in sizing the system.
As you explore options, remember that not every location is perfect for solar. Weather conditions and local regulations can impact efficiency. Consider conducting a professional assessment for tailored solutions to maximize your investment.
Types of Solar Power Systems: Photovoltaic vs. Solar Thermal Solutions
When exploring solar power systems, two main types emerge: photovoltaic (PV) and solar thermal.
Photovoltaic systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using solar panels. This technology has gained significant traction due to declining costs and increased efficiency.
A report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) indicated that the global solar PV capacity reached over 800 GW in 2021, marking a 23% increase from the previous year.
On the other hand, solar thermal solutions utilize sunlight to produce heat, which can be applied for water heating or space heating. This system tends to be less popular than PV but is effective in specific applications.
According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), solar thermal still contributes significantly to renewable energy capacity, particularly in areas with high hot water demand.
Both systems have their pros and cons. PV systems can be more versatile and suitable for electricity generation, while solar thermal can achieve higher efficiency in heating applications.
However, efficiency can vary due to weather conditions and geographical location. Understanding these differences is crucial for homeowners aiming to make informed choices about solar energy.
The choice between the two depends on individual needs and existing infrastructure.
Evaluating Your Home's Solar Potential: Key Factors and Industry Standards
Evaluating your home's solar potential begins with understanding your geographical location. Sunlight availability varies widely across regions. Areas closer to the equator typically receive more sunlight. Consider shading from trees or nearby buildings. A shaded roof will produce less energy, making solar panels inefficient.
Next, examine your rooftop's orientation and angle. South-facing roofs usually get the most sunlight. An ideal pitch can maximize energy capture. If your roof isn't suitable, consider ground-mounted systems. Local regulations might affect installation options, so check before proceeding.
Finally, assess your energy needs. Review past utility bills to understand your consumption patterns. Estimate how much energy you want to generate with solar panels. Remember, overestimating can lead to wasted money. Balancing energy production and usage is essential for effective solar investment. This requires ongoing evaluation and adjustment, as your needs may change over time.
How to Harness Solar Power for Your Home Energy Needs? - Evaluating Your Home's Solar Potential: Key Factors and Industry Standards
| Factor | Description | Impact on Solar Potential |
|---|---|---|
| Roof Orientation | Direction your roof faces affects sunlight absorption. | South-facing roofs receive the most sunlight. |
| Roof Angle | The steepness of your roof can influence solar panel effectiveness. | Optimal angles can increase energy production. |
| Shade Analysis | Shade from trees, buildings, or other obstructions. | Less shade equals more energy generation. |
| Local Climate | Weather patterns and sun exposure in your area. | Warmer, sunnier climates generally yield better results. |
| Panel Efficiency | Rating of how much sunlight is converted to electricity. | Higher efficiency leads to better energy output. |
| Inverter Quality | Quality of the device that converts DC to AC power. | Better inverters enhance system performance. |
| Government Incentives | Subsidies and rebates available for solar installations. | Can significantly reduce initial costs. |
Sizing Your Solar Energy System: Calculating Energy Needs and Output
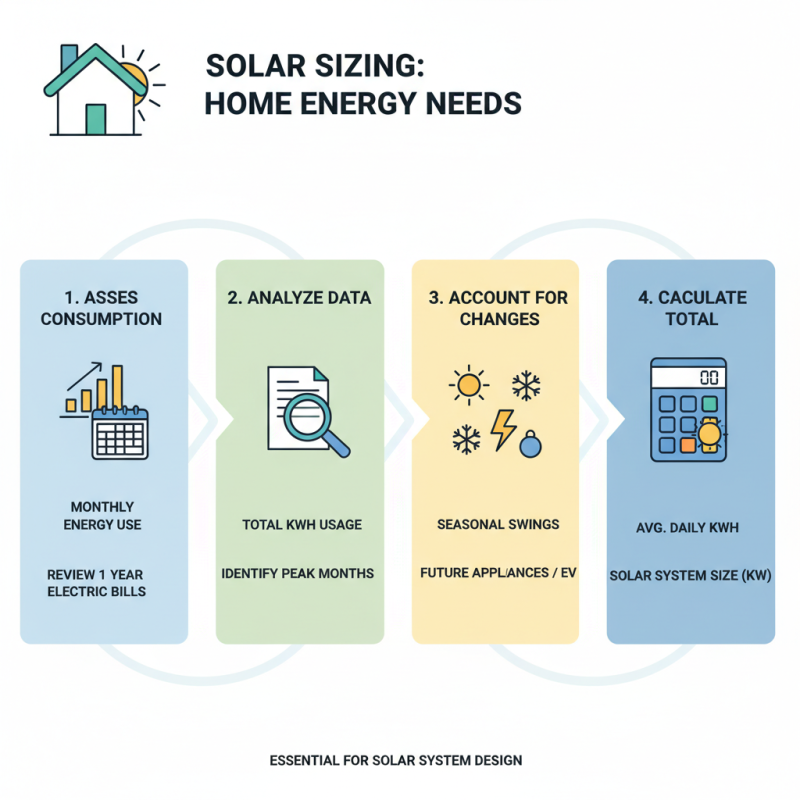
Calculating your home's energy needs is essential for sizing a solar energy system. Start by assessing your monthly energy consumption. Look at your electricity bills for a year. This gives you a clear idea of how much power you use. Don't forget to include peak usage months and any seasonal changes.
Next, consider your location. The amount of sunlight varies by region. Some areas receive abundant sun, while others do not. Understanding your average solar output can help you plan. You might think a larger array is always better. However, this may not be the case. Overestimating sunlight can lead to excess capacity.
Evaluate your appliances as well. Not all electrical devices have the same energy requirements. Smaller appliances may be easier to power, but larger ones like air conditioners need more attention. You might not account for future energy needs. If you plan to add new devices, factor those into your calculations. Remember, accurate sizing requires careful thought and adjustments over time.
Incentives and Financing: Leveraging Government Programs for Solar Adoption
In recent years, government programs have become pivotal for solar adoption. Incentives such as tax credits can significantly reduce initial costs. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association, the federal solar tax credit is now 26%. This incentive allows homeowners to claim a percentage of installation costs on their taxes. States also offer grants and rebates, making solar more accessible.
Tips: Research local programs for maximum benefits. Sometimes, installation companies help navigate these options. These resources can lighten the financial load but require due diligence. Not all programs are widely advertised. Some might need more outreach.
Financing options range from traditional loans to innovative models like power purchase agreements. Homeowners can explore low-interest loans that require minimal upfront fees. Yet, not all financing paths offer equal returns. It's crucial to assess long-term savings versus interest payments. Remember, impulse decisions can lead to financial strain. Carefully compare rates and terms to find the right fit for your situation.
Related Posts
-

Uncover the Excellence of Best Solar Engineering from Chinas Leading Manufacturers
-

The Future of Future Solar Technology and Its Impact on Renewable Energy Trends
-

Unlocking the Advantages of the Best Solar Energy Solutions for Sustainable Living
-

Understanding the Advantages of Best Solar Structure Solutions
-

Navigating Industry Standards: Challenges in Sourcing the Best Green Solar Panels Globally
-

Setting Industry Standards for the Best Solar Energy Solutions: A Path to Sustainability